This problem includes three reservoirs connected by three pipes with an additional external flow demand at the common junction of the three pipes. The highest reservoir has a water surface elevation of 100.0 M, the middle reservoir water surface elevation is 85.0 M and the lowest reservoir has a water surface elevation of 60.0 M.
The pipe from the highest reservoir has a length of 2000 M and an inside diameter of 300mm. The pipe from the middle reservoir has a length of 1500 M and inside diameter of 250mm and the pipe from the lowest reservoir has a length of 3000 M and inside diameter of 250mm. The absolute pipe roughness of each pipe is 0.0005 m.
We are required to determine the discharge in each pipe. 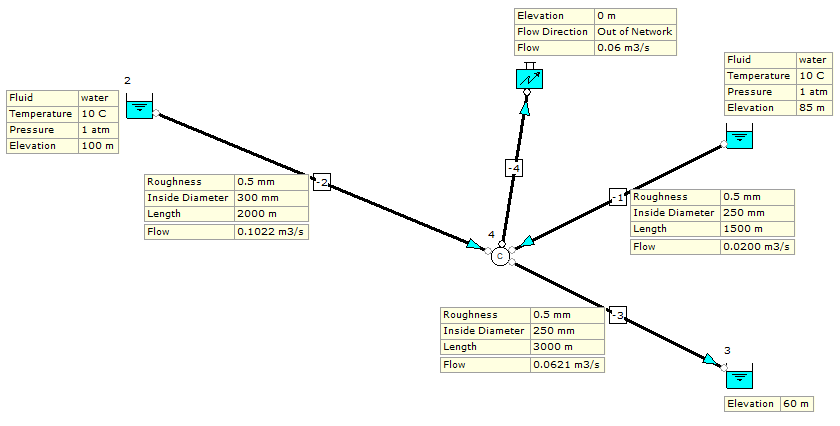
Fig 1: Three Reservoir Problem.
| Description | Published Results | FluidFlow Results |
| Flow rate from highest reservoir | 0.1023 m3/s | 0.1022 m3/s |
| Flow rate from middle reservoir | 0.02 m3/s | 0.02 m3/s |
| Flow rate from lowest reservoir | 0.0622 m3/s | 0.0621 m3/s |