FluidFlow calculates the K Straight and K Branch values for Idelchik tees as follows:
Kb = Kt / (Vb / Vch)2
Kst = Kt / (Vst / Vch)2
Let’s consider the QA Example as follows:
Kb = Kt / (Vb / Vch)2
(Vb / Vch)2 = (3.141 / 6.131)2 = 0.262466.
Branch K = 0.4328, therefore Kt = 0.4328 / 0.262466 = 1.65 or 1.64897 to be more accurate.
Kst = Kt / (Vst / Vch)2
(Vst / Vch)2 = (2.99 / 6.131)2 = 0.237837.
Branch K = 0.5292, therefore Kt = 0.5292 / 0.237837 = 2.2244.
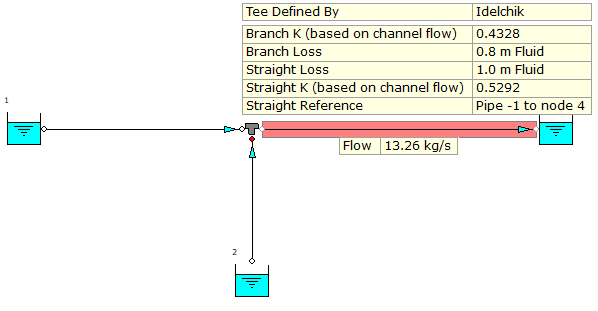
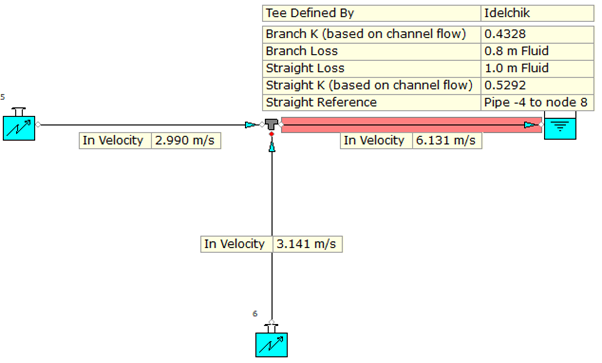
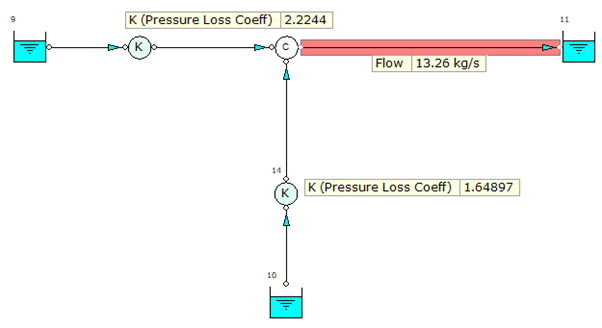
If we have a look at the models above, we can see a number of scenarios;
- An Idelchik tee model developed based on design pressure inlets.
- The same model developed using known flow inlets at the boundaries.
- The same type of model developed using pressure loss coefficient nodes where the K values have been defined. The results are identical across all three models.
Note, the K values found in the Idelchik Handbook are based on volumetric flow in the “channel”.