Let's say we have heat energy of 40 kW at a piece of equipment (heat exchanger etc) and we know the pressure loss for this item is approx. 15 l/min @ 0.6 bar. We can define this condition using a Kv node as shown below.
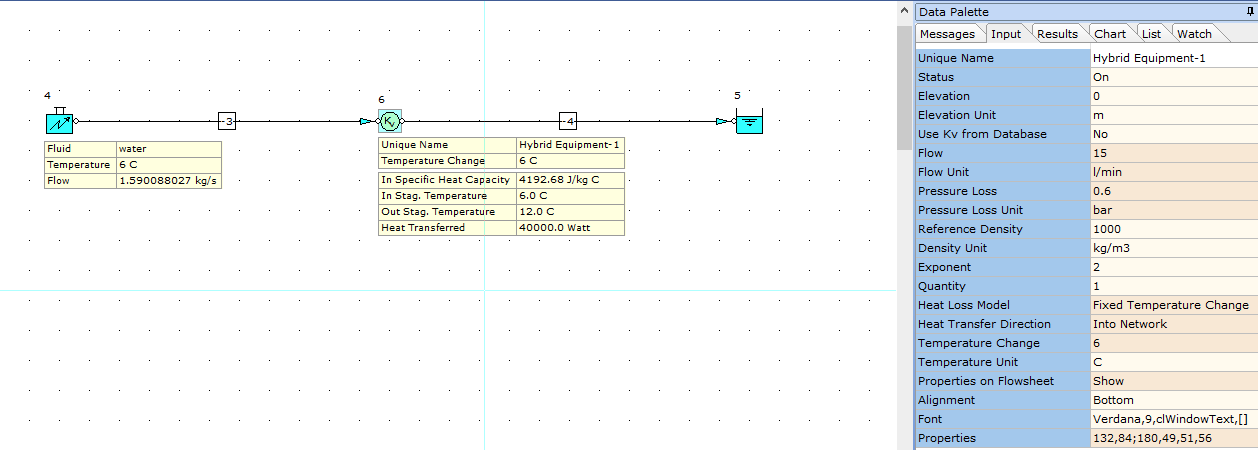
In terms of heat transfer, we know we have 40 kW of heat energy transfer at the piece of equipment (node 6) and lets say our design operating temperatures are 6 degrees C flow and 12 degrees C return, i.e. 6 degrees Delta T.
We can therefore estimate the required mass flow rate for the equipment as follows:
Q = m Cp * Delta T
m = Q / Cp * Delta T
m = 40 / 4.19268 * (12 - 6)
m = 1.590088027 kg/s.
We have therefore defined this mass flow rate for the system and a fluid flow temperature at the inlet boundary of 6 degrees C. We can see that based on the defined heat transfer value of 40 kW at node 6, the resultant outlet temperature at this node is now 12 deg C which was the basis of the design calculation above.
So we can see above, we can use a Kv to represent any device and also model heat transfer at this node (or any node).
Note, if you don't want to define a fixed flow rate in your system and wish to model tanks, you can of course use an orifice plate or flow control valve to balance the system flow rates. In the above case, we could have used a known pressure at the inlet, inserted an orifice plate and set the RO to be sized on a design flow rate of 1.590088027 kg/s.